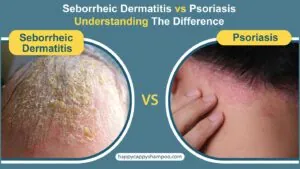
Seborrheic Dermatitis is extremely common in babies. The opposite is true of scalp psoriasis. Infant psoriasis is considered a rare condition. It tends to affect people between the ages of 15 and 35 far more than those under the age of 10.
It’s easy to understand why adults could confuse the two. Both skin conditions affect the scalp and can cause red, scaly skin. To know the difference between these conditions, it is important to understand them.
What Is Seborrheic Dermatitis (Cradle Cap)?
Seborrheic dermatitis or cradle cap in babies is considered a severe form of dandruff. It causes inflammation, itching, and flaking of the skin. Seborrheic dermatitis can appear anywhere on the body, but the most common places are the scalp, eyebrows, ears, nose, and forehead.
When it appears in babies, it can cause thick, crusty scales that cover the baby’s scalp, like a cap. In babies, it also frequently appears in the armpits, and in the groin folds in the diaper area.
Seborrheic Dermatitis Causes
Even though the exact cause of seborrheic dermatitis is still not known. But the scientists and researchers believe it is caused by a combination of factors like
- Overactive sebaceous glands
- Malassezia yeast
- Overproduction of sebum
When the sebaceous glands start producing excess sebum, it provides a breeding ground for the Malassezia yeast that is naturally present on the skin.
When Malassezia yeast and sebum combine, they create a byproduct, oleic acid, that causes inflammation, scaling, and flaking on the skin.
What Is Psoriasis?
Psoriasis is a chronic skin condition that causes the skin cells to grow at a much faster rate, even before the dead skin cells fall off. These cells accumulate on the skin and cause scaly patches.
Psoriasis patches can appear anywhere on the body. However, the most common places are the scalp, elbows, and knees. Psoriasis has five common types; each may manifest differently, but scaly patches are common.
- Plaque psoriasis (Most common)
- Guttate psoriasis
- Inverse psoriasis
- Pustular psoriasis
- Erythrodermic psoriasis
Psoriasis Causes
Psoriasis is believed to be caused by an autoimmune disorder. Our immune system protects our body and skin from outside bacteria and allergens by releasing a certain type of cells known as T-cells.
When there is an issue with the immune system, it releases those T-cells even when no bacteria is attacking the body. These cells then start attacking the skin, causing the production of new skin cells to speed up. The accumulation of these cells results in thick, scaly patches.
Psoriasis VS Seborrheic Dermatitis Symptoms
The best way to distinguish seborrheic dermatitis and psoriasis is by identifying their symptoms. The doctor will also diagnose your condition by looking at your symptoms.
Seborrheic Dermatitis Symptoms
- Inflamed skin
- Itchy skin
- Oily, greasy patches
- Redness
- Yellow or brown colored scales
- Scaly skin
- Thick, crusty scales (cradle cap)
Psoriasis Symptoms
- Dry skin
- Itching
- Raised skin patches
- Silvery-white skin scales
- Skin cracking
- Bleeding
- Burning sensation
Difference Between Seborrheic Dermatitis VS Psoriasis
| Seborrheic Dermatitis (SB) | Psoriasis | |
|---|---|---|
| Causes | Malassezia yeast, overactive sebaceous glands | Autoimmune disorder |
| scales | Yellow or brown-colored greasy scales | White or silver-colored scales |
| Itching | Mild itching | Severe itching |
| Burning sensation | Very rare | On the scales |
| Appearance of flakes | Flakes are greasy to the touch | Flakes are dry to the touch |
| Age | It affects people above 30 and babies under 12 months (cradle cap) | It is more common between the ages of 15 and 35. |
Diagnosis
A doctor can determine which skin condition is causing your symptoms with an examination of the scalp, skin, and nails. Psoriasis tends to be more difficult to treat than Seborrheic Dermatitis and comes with its own unique set of dietary, medical, and environmental triggers. So, the approach to managing psoriasis will be different than with Seborrheic Dermatitis.
Treating Seborrheic Dermatitis VS Psoriasis
Seborrheic Dermatitis Treatment
The best way to manage the itching, flaking, and inflammation associated with seborrheic dermatitis and cradle cap is by washing the affected area with a medicated shampoo. Use a cradle cap shampoo that contains pyrithione zinc as an active ingredient.
- Wash the scalp and affected area with a cradle cap and seborrheic dermatitis shampoo.
- Shampoo daily when seborrheic dermatitis flare-ups.
- Once the flaking and scaling has reduced, shampoo 2 to 3 times a week.
- While shampooing, gently massage the skin with your fingertips, washcloth, or a cradle cap brush.
Try Happy Cappy Medicated Shampoo For Cradle Cap, Seborrheic Dermatitis, and Dandruff it contains pyrithione zinc, which helps in reducing the growth of Malassezia yeast. It is free from harsh chemicals like paraben, sulfate, fragrances, and dyes. It can help reduce flaking and scaling associated with seborrheic dermatitis (a.k.a. cradle cap) without irritating the skin.
To get the best results, try using the Happy Cappy Bath Bundle. It includes a cradle cap shampoo and a cradle cap brush to help you get rid of those scales fast.
Psoriasis Treatment
Psoriasis needs proper treatment. It requires attention from a dermatologist who may prescribe Topical corticosteroids to help reduce the inflammation and the growth of skin cells.
In some cases, a combination of oral and injectable medication may be used to control psoriasis. Light therapy is also used to manage it.
Conclusion
In conclusion, seborrheic dermatitis and psoriasis may cause redness and scaly patches, but these are two different skin conditions. Their causes and symptoms are different, and so are their treatments.
Seborrheic dermatitis can be easily managed at home with the use of a seborrheic dermatitis shampoo. However, psoriasis needs a different level of treatment and attention.
FAQs
- Eczema VS Psoriasis: Discovering the Difference - February 24, 2025
- Eczema on Black Skin: Is It Different? - February 24, 2025
- Scalp Health – A Reflection of What We Eat? - February 24, 2025
Is seborrheic dermatitis psoriasis?
Both conditions may appear as red, scaly patches with itch, but they have different underlying causes and distribution on the body. Overactive sebaceous glands cause seborrheic dermatitis, while psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune disorder.
How is psoriasis diagnosed?
o diagnose psoriasis, your healthcare provider will first examine the affected skin, nails, and scalp. They will inquire about your medical history and family history of psoriasis. Sometimes, they may perform a skin biopsy if there is still a doubt.
What is another name for seborrheic dermatitis?
Some other common names for seborrheic dermatitis are dandruff, cradle cap, seborrheic eczema, and Seborrhea.
Is seborrheic dermatitis permanent?
Seborrheic dermatitis is a chronic condition that may come and go and sometimes throughout the lifetime. It can not be completely cured but effectively managed through proper care and treatment.
Can you have seborrheic dermatitis and psoriasis at the same time?
Yes, one can have seborrheic dermatitis and psoriasis at the same time.
Is the treatment for psoriasis and seborrheic dermatitis the same?
The initial treatment for both conditions is the same, which is the use of medicated shampoo. The rest of the treatment is different as the underlying cause for each condition is different. So, the healthcare provider will provide you with a treatment plan that best suits your condition.