
Have you noticed acne or bumps on your little one’s skin?
Fungal acne and closed comedones can look similar to each other, especially if you don’t have a background in dermatology. To make things more complicated, fungal acne can sometimes cause closed comedones.
Recognizing exactly what those bumps are is the first step to controlling the symptoms. Are closed comedones fungal acne? They can be, but they aren’t always. Both skin conditions are distinct, so it’s important to understand the differences between fungal acne vs closed comedones.
Let’s take a closer look at their symptoms, causes, and differences.
What is Fungal Acne?
Fungal acne, also known as Pityrosporum folliculitis or Malassezia folliculitis, causes small bumps to appear on your skin that look similar to regular acne. The overgrowth of Malassezia yeast in the hair follicles is believed to cause this condition.
It can cause itchy, inflamed pustules and papules. As the Cleveland Clinic points out, those bumps can eventually become whiteheads. And a whitehead is a closed comedone. This is why both conditions are often confused with each other.
What Causes Fungal Acne?
In the simplest terms, fungal acne is caused by a fungal infection. More specifically, it involves a yeast called Malassezia. This yeast feeds on sebum, an oily substance that comes from the sebaceous glands present in every person. This is the same yeast that causes dandruff and seborrheic dermatitis.
Sebum is natural and beneficial. Unfortunately, it can also fuel the Malassezia yeast. Newborns can have higher levels of Malassezia than people in other age groups. That can make the overgrowth of yeast, and fungal acne, more common for babies.
The yeast can enter hair follicles and sebaceous glands. When it does, the body produces an immune response. That includes inflammation, which leads to small red bumps called papules.
What Does Fungal Acne Look Like?
It looks similar to the acne we experience in our teenage years. They appear as small bumps covered with skin that can sometimes be white, red, or skin-colored. Some other common symptoms that you may notice if you have fungal acne are:
- Itchy skin
- Pustules and papules
- Bumps of the same size and shape
- Irritated skin
- Inflammation
- Redness
- Pus-filled bumps
- Stinging sensation
Fungal acne can appear anywhere on the body where hair follicles are present. However, some of the most common areas are:
- Cheeks
- Forehead
- Chest
- Upper back
- Neck
Another sign that you may have fungal acne is that it does not respond to normal acne treatment.
What Are Closed Comedones?
A ghostwriter doktorarbeit closed comedone is a type of pimple commonly called a diplomarbeiten schreiben lassen whitehead. That name is very descriptive, as whiteheads look like raised bumps with a whitish interior. They can be caused by fungal acne or without an infection when sebum and dead skin clog a hair ghostwriter-texte follicle.
Remember that fungal acne is a specific type of acne, while a closed comedone is a specific type of pimple. Is your skin condition closed comedones or fungal acne? Sometimes, it can be both because fungal acne can also cause ghostwriting kosten closed comedones.
These are further divided into two types:
- Microcomedones: These are very small in size barely visible to the naked eye.
- Macrocomedones: These are a little larger in size, around 2 to 3 millimeters in diameter.
What Causes Closed Comedones?
Closed comedonal acne is caused when your pores become clogged with dirt, dead cells, oil, and debris. This is why it gets the name closed, and blackheads get the name open comedones as they are partially clogged pores.
There are various factors that can trigger whiteheads to appear on your skin, and hormonal changes in the body is one of the most common. This is why we often experience acne in puberty, during pregnancy, and menopause. Hormonal changes in the body can trigger the skin to start producing more sebum that can mix with dead skin cells, dirt or bacteria and clog the pores.
Some other common factors are:
- Unhealthy diet
- Oily skincare products
- Smoking
- Alcohol consumption
- Not exfoliating the skin
- Air pollution
- Humidity
Sometimes a single factor can cause the condition while other times 2 or 3 factors work together to give you those bothersome pimples.
What do Closed Comedones Look Like?
Closed comedones appear as small red, white, or skin-colored bumps, just like you have in fungal acne. However, pain and inflammation are not its symptoms.
These are more common in areas of the body with an abundance of sebum, such as:
- Cheeks
- Face
- Chest
- Back
- Neck
- Chin
Now that we have understood what these two common types of acne are, let’s discuss their differences.
Difference Between Fungal Acne Vs Closed Comedones
If you’re wondering if you or your child has Malassezia folliculitis fungal acne vs. closed comedones, the answer can be both. Both conditions cause small white or skin-colored bumps on the skin, which can easily confuse you.
However, a key difference between fungal and other types of acne is that fungal acne often causes itching, while others do not. The presence or absence of an itching sensation can help you tell the difference.
Here are some other differences to help you understand whether you have fungal acne or closed comedones.
| Fungal Acne | Closed Comedones | |
| Appearance | Small bumps that may have redness around them and are of similar size and shape | Small Bumps covered with skin with whiteheads of different shapes and sizes |
| Location | Forehead, face, chest, back, | Nose, forehead, cheeks, chin |
| Itching | Intense itching | Very rare |
| Causes | Overgrowth of Malassezia yeast | Clogged pores, excess sebum, hormonal imbalance |
| Triggers | Warm, humid environment, sweating | Genetics, hormonal changes, skincare products |
| Inflammation | Yes | No |
| Feeling | Burning or stinging sensation | No itchy feeling or pain |
| Treatment | Anti-fungal treatment | Topical treatment |
| Spread | It can spread to other areas of your body through contact | It does not spread to other parts of the body by touching. |
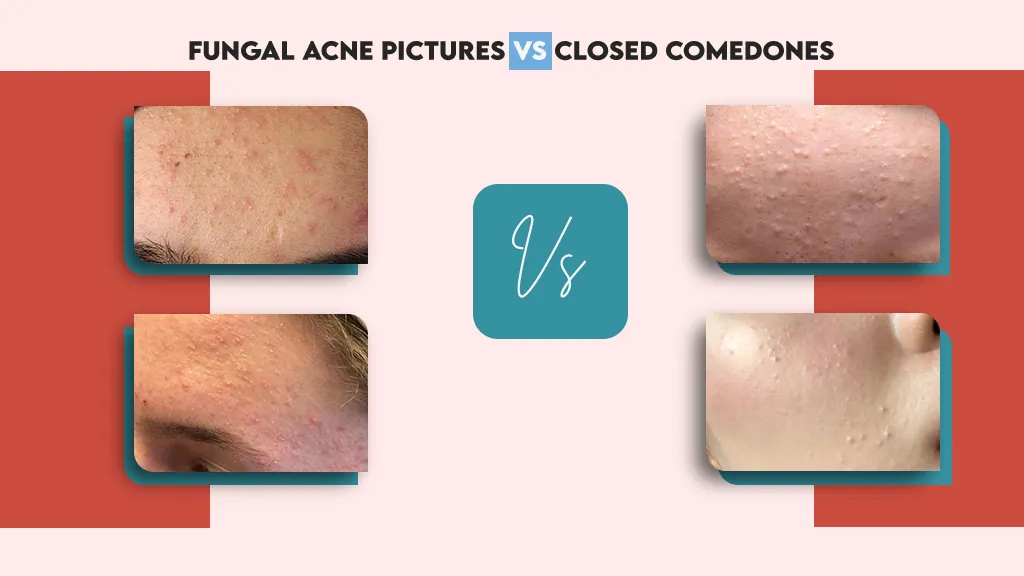
Fungal Acne Pictures vs Closed Comedones
Treating Closed Comedones Vs Fungal Acne
Just like the cause for both the conditions is different their treatment is also very different. Fungal acne will not get better if you keep on using the treatment you do for regular acne. Here is an overview of the different treatment options for each condition.
| Fungal Acne | Closed Comedones | |
| Skincare routine | Use non-comedogenic and antifungal skincare products | Water-based, non-comedogenic products. |
| Topical treatment | Anti-fungal creams like ketoconazole, clotrimazole | Retinoid creams, salicylic acid |
| Oral medication | Fluconazole, itraconazole | Oral retinoids, hormonal treatments |
| Professional treatment | Laser treatment, micro needling | Microneedling, extraction, chemical peels |
Fungal Acne Treatment
Maintaining a healthy skin microbiome is essential for treating and preventing fungal acne. This can only be done by following a proper fungal acne skincare routine and keeping your skin clean. The first thing that you must do is to keep your skin clean with a fungal acne cleanser.
Wash your face with fungal acne face wash at least twice daily, once in the morning and once before going to bed. Using a cleanser that contains pyrithione zinc as an active ingredient can help control the growth of Malassezia yeast and reduce the appearance of acne.
If your condition does not get better with the use of a cleanser then consult a dermatologist they may prescribe the use of OTC antifungal creams and oral anti-fungal medications to help reduce the symptoms.
Closed Comedones Treatment
Treating closed comedones requires persistence in following a proper skincare routine.
- The first step in this routine is to cleanse the skin with an acne face wash or cleanser.
- The second step is to exfoliate the skin at least once a week.
- And the third step is to moisturize your skin with a non-oily moisturizing cream.
When you choose your products, make sure that they are non-comedogenic and oil-free, as oil in the products can further exacerbate your condition. If this routine does not make much difference, then the doctor may prescribe topical retinoids, which enhance skin cell turnover and prevent clogging. In severe cases, laser treatment and closed comedone extraction is done to get rid of the pimples.
Preventing Acne
Once you get rid of your acne, whether fungal or hormonal, it can still reappear. But you can add a few simple things to your daily routine to prevent future breakouts.
- Cleanse your skin regularly.
- Exfoliate your skin once a week gently.
- Use water-based moisturizers instead of oily ones on your skin.
- Keep your body and skin hydrated by drinking almost eight glasses of water daily.
- Eat a well-balanced diet, and avoid consuming fatty, oily food.
- Never sleep with makeup on your face.
- Wash your face after heavy activities and sweating.
The key to preventing acne is keeping your skin clean and moisturized and avoiding clogging of pores.
Shop Happy Cappy Products

If you are experiencing fungal or neonatal acne, try Happy Cappy medicated Shampoo and Body Wash. It can also be used as a face wash and is safe for babies, teenagers, and adults.
It is free from any skin-irritating chemicals such as fragrances, sulfates, parabens, and phthalates. Try Happy Cappy Products to soothe your baby’s and your skin.
Conclusion
Fungal acne appears when the hair follicles become infected due to the overproduction of Malassezia yeast on the skin. This leads to itchy, small bumps on the skin and inflammation.
Closed comedones or whiteheads occur when the pores become clogged by oil, sebum, dirt, and dead skin cells. Although both conditions cause similar-looking bumps on the skin, they are different.
The treatment for these conditions is also different, the treatment that you use for regular acne or closed comedones will not work for fungal acne. Fungal acne can be treated with the help of anti-fungal cleansers, creams, and medication.
FAQs
How do I know if I have comedonal or fungal acne?
It can be difficult to tell fungal and comedonal acne apart. Fungal acne usually causes inflammation and itching along with small bumps. But if you have comedonal acne it will not be itchy or inflamed.
The treatment and medication used to treat comedones will not make your fungal acne better.
Can you have closed comedones and fungal acne at the same time?
Yes! There is a chance that you will experience both at the same time because fungal acne can often cause closed comedones to appear on the skin.
What does the start of fungal acne look like?
When fungal acne first appears, it causes a red rash with a cluster of bumps that are the same size and shape. These bumps can be itchy and inflamed.
What worsens fungal acne?
Fungal acne is caused by Malassezia yeast, and anything that triggers its growth, such as oil on the skin, excessive sweating, humid weather, and a compromised immune system, can worsen the condition.
Why am I suddenly getting closed comedones?
The main reason why you are experiencing closed comedones is that your skin pores are clogged and blocked with sebum, dirt, or dead skin cells. Not keeping the skin clean and hormonal changes in the body are the most common reasons for clogged pores.
Can you pop closed comedones?
Never pop your closed comedones, pustules, and papules. When you touch or pop the bump the bacteria from your hands are transferred to the breakouts that can worsen the condition and cause inflammation. It can also lead to other complications like skin infections and skin scarring.
How do dermatologists remove closed comedones?
The dermatologist will first prescribe the use of topical cream or medication to get rid of the closed comedones. If they still don’t get better they may manually extract them.
