According to the National Eczema Association, eczema, also known as atopic dermatitis, affects around 31.6 million Americans annually. And one of the most famous myths about this skin condition is that you can catch it from someone else, but is it really true? Is eczema contagious?
Read this blog to discover the truth.
What is Eczema?
Eczema is a common inflammatory skin condition that causes red, inflamed, and often itchy rashes on the skin. Though it may look unsightly, having eczema doesn’t mean that the skin is infected or dirty.
It is a chronic skin issue, which means it may resolve forever, or in most cases, it may come and go as a period of remission and flare-ups. Most people who experience eczema are first diagnosed with it before the age of 6.
However, this does not mean that if you didn’t have eczema when you were young, you can’t have it as an adult. Adult-onset eczema is also a common issue.
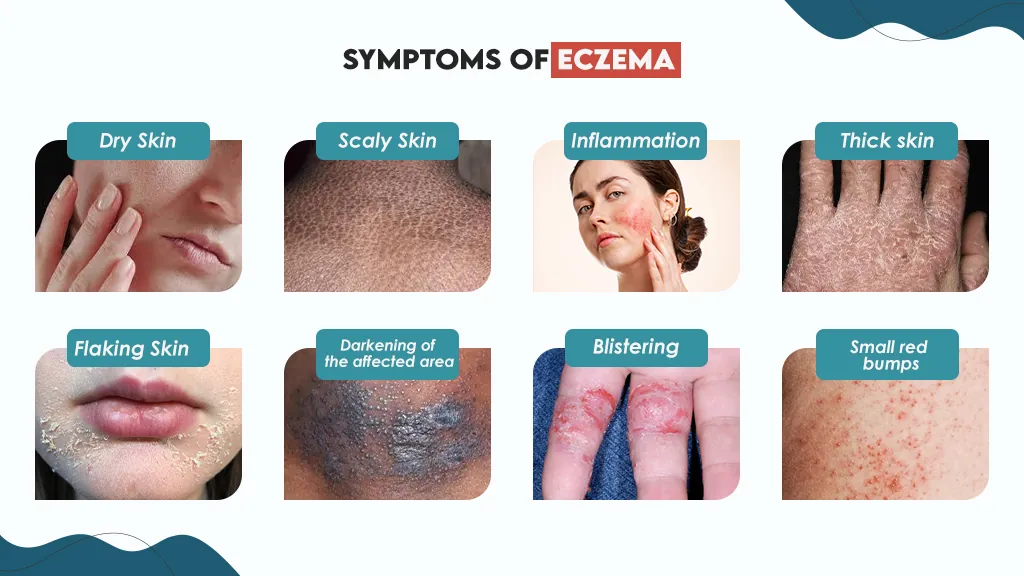
Symptoms of Eczema
Unfortunately, doctors are still working on determining the exact cause of eczema. However, the experts are currently theorizing that the condition stems from a combination of genetics and the environment.
When the body comes into contact with an allergen or irritant, it switches on the immune system to fight it off. Doctors think that people with eczema are genetically missing certain skin proteins that help protect it from outside allergens, therefore making the skin more susceptible to irritation and an over-aggressive immune response that can cause:
- Dry skin
- Scaly skin
- Inflammation (swelling, redness, and warmth of the area)
- Thick skin
- Flaking skin
- Darkening of the affected area
- Blistering
- Small red bumps
But an eczema rash generally doesn’t just pop up out of nowhere. The rash is usually in response to an environmental irritant called a trigger. While triggers can differ slightly from person to person, the most common are things like food allergies, irritating fabrics like wool, harsh ingredients in cleaning and skincare products, dry air, extreme temperature, and fragrances.
Is Eczema Contagious?
The simple answer to the question, “Is atopic eczema contagious?” is NO. It is not contagious, and it can not be spread from one person to another by breathing, touching, or coming in contact with it.
It is not a virus (like Coronavirus) or a bacteria or a pathogen that can be transmitted. Even though the eczema rash looks concerning, and some people may think that they will catch it from touching it, it is simply not true.
However, skin damage due to eczema flare-ups can make it easier for bacteria and viral infections to enter your body and lead to infections that can be contagious.
Can Eczema Spread to Other Parts of the Body?
Although eczema is not contagious and cannot be passed on to others, it can spread to other parts of the body, especially during a flare-up. We all know that during a flare-up, those iconic symptoms of eczema, itching, redness, irritation, and inflammation become even worse.
All these symptoms becoming severe can lead to intense itching that can be very hard to resist. When you scratch that rash, it becomes more inflamed and can easily spread or more accurately–it can become visible on other parts of the body as well.
Proper treatment is essential if you are experiencing a severe eczema flare-up. Otherwise, you might end up spreading it to other body parts, leading to complications like skin infections and scarring.
Can Eczema Get Infected?
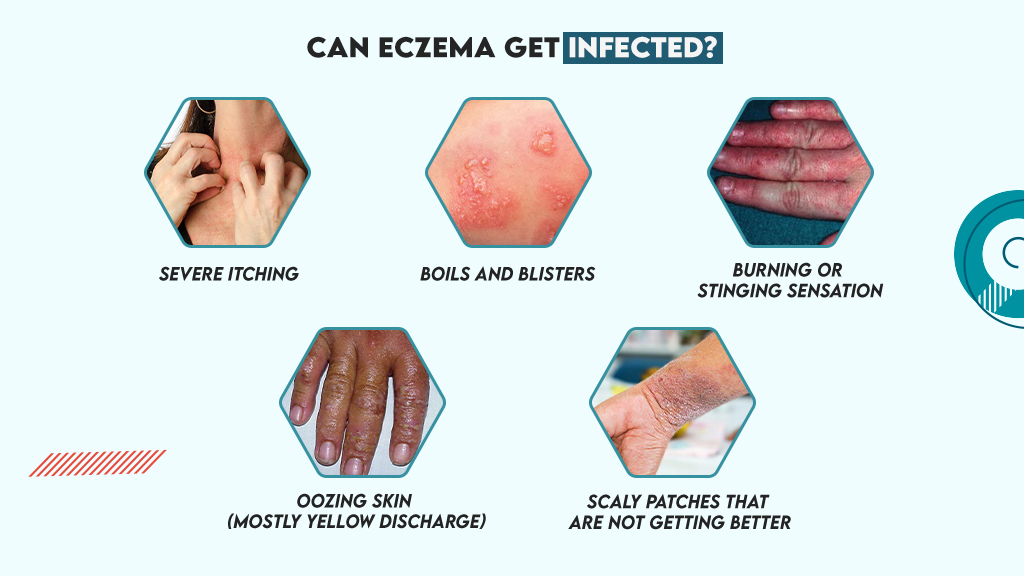
Yes, eczema can get infected When proper care and treatment are not provided to the skin, it can lead to infections. Some common symptoms that you will notice if your eczema is infected are:
- Severe itching
- Boils and blisters
- Burning or stinging sensation
- Oozing skin (mostly yellow discharge)
- Scaly patches that are not getting better
Eczema tends to disrupt your skin’s natural barrier, making it easier for outside bacteria and viruses to penetrate the skin. And if you scratch your eczema, the chances of developing skin infections increase.
Some of these skin infections can be contagious. Some of the most common infections associated with eczema are:
- Eczema herpeticum
- Streptococcus
- Staphylococcus
- Dermatophytes
- Candidiasis
If you suspect that your eczema is becoming infected, contact a dermatologist immediately to get the right treatment plan and prevent further complications.
Similar Conditions That Are Contagious
Various other conditions, like psoriasis, ringworm, and rosacea, cause symptoms similar to those of eczema, making it difficult for a normal person to distinguish them. Some medical conditions that look similar to eczema can be contagious.
Some of the conditions that can make you think that you have eczema and can spread it to others are:
- Molluscum dermatitis
- Impetigo
- Herpes virus
- Syphilis
These conditions can irritate your skin, lead to redness, and cause small bumps and blisters to appear on the skin. If you are unable to rule out whether you are experiencing eczema or something else then it is best to consult a doctor.
Eczema Treatment
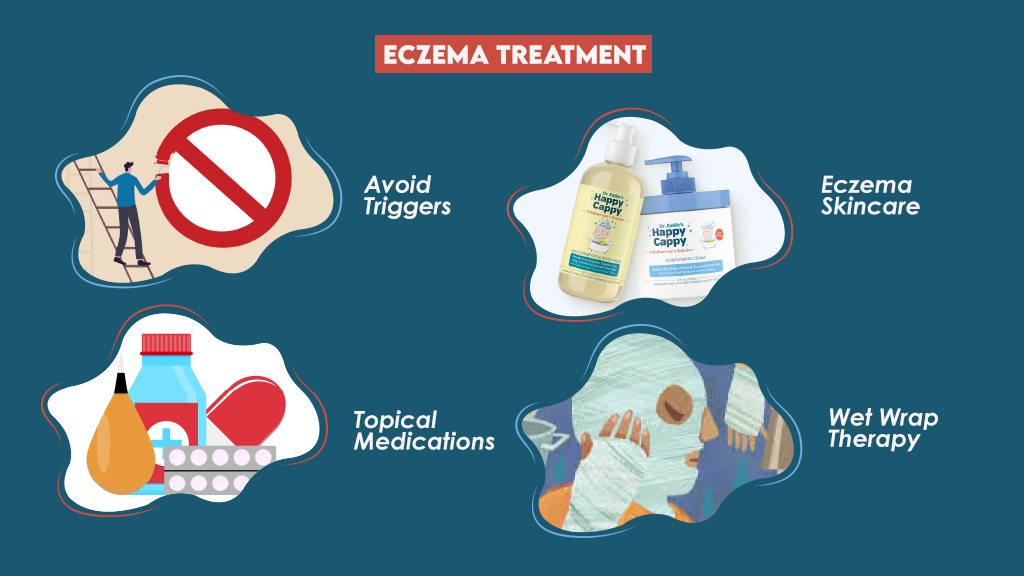
Though there is no permanent cure, the most effective way to treat eczema symptoms is a combination of trigger management and proper skincare.
Avoid Triggers
Since the inflammatory response is brought on or worsened by triggers, a great way to avoid that response is to avoid the triggers. Since every person’s triggers may be slightly different, the first step in trigger management is determining your specific triggers.
Take note of when you get an eczema flare-up and what you have come into contact with in the days prior. Did you try a new shampoo or laundry detergent? Was it particularly hot or cold outside? If there are similarities from flare-up to flare-up, those are probably your triggers. Do your best to avoid them.
Eczema Skincare
The second piece of eczema treatment is proper skincare. Eczema-prone skin has a weakened moisture barrier, so you need to develop a skincare routine that helps strengthen that barrier and protect the skin from irritants.
Step 1
The first step is to use an eczema shampoo and body wash that is specially formulated for sensitive eczema-prone skin. Use it to clean your skin at least once daily, two times is best if you can do that.
Remember to clean your skin every time you come from outside to get rid of the bacteria and viruses that can infect your eczema rash.
Step 2
The second step in proper skin care is regular moisturizing. Hydrated skin is healthy skin, so use an eczema moisturizing cream at least twice a day to help lock in moisture and keep the skin safe from irritants.
If your skin gets dry more often, you can increase the use of moisturizer. However, make sure to use a moisturizer free from irritating chemicals like fragrance, sulfate, paraben, and phthalates.
Opt for a moisturizer like Happy Cappy Moisturizing Cream for Eczema that is known as 100% safe for sensitive skin by SkinSAFE.
Topical Medications
If the eczema skincare routine is not doing much good for your condition, then a physician may prescribe the use of certain medications, such as:
- Topical corticosteroids
- Topical calcineurin inhibitors
- Antihistamines
These medications should only be used as prescribed by a doctor, because using these for an extended period of time inappropriately can lead to other skin issues.
Therapy
In some cases, mostly when the itching is severe, a doctor may prescribe wet wrap therapy. In this type of therapy, a topical medication is applied to the affected area which is then covered with a wet gauze followed by a dry cloth.
This can be beneficial for people who experience intense itching at night. This therapy helps soothe the itching as it can be applied overnight and helps you sleep better.
Conclusion
Eczema is not contagious, and you can not get it from someone else. If you are experiencing eczema, your genetics and other environmental factors are to blame.
However, during an eczema flare-up, scratching your rash can worsen the condition and cause the rash to spread to other parts of the body. Scratching the rash can also make your skin more prone to developing secondary infections, which can be contagious.
You can manage an eczema flare-up and prevent future ones by avoiding the triggers that make your condition worse, keeping your skin clean with an eczema cleanser, and keeping it moisturized at all times with an eczema cream.
Shop Happy Cappy Products today and say hello to itch-free, hydrated, soft skin.
FAQs
Can you get eczema from someone else?
No, you can not get eczema from someone else. It is not caused by bacteria, viruses, or pathogens, so it is not contagious.
Does eczema spread by scratching?
Scratching your eczema will not cause it to spread to others. However, it can spread to other parts of your body from scratching.
Why do I suddenly have eczema?
Even though genetics is to be blamed for eczema, various triggers around us actually cause it to develop, such as dry air, extreme weather conditions, reactions to chemicals in skincare products, and harsh fabric.
These triggers can cause a reaction on your skin, leading to the itching, redness, and irritation associated with eczema.
Does eczema ever go away?
Eczema is a chronic skin condition, which means it is likely to appear again as a flare-up. In most cases, people experience flare-ups throughout their lives, while for others, it may disappear completely over time.